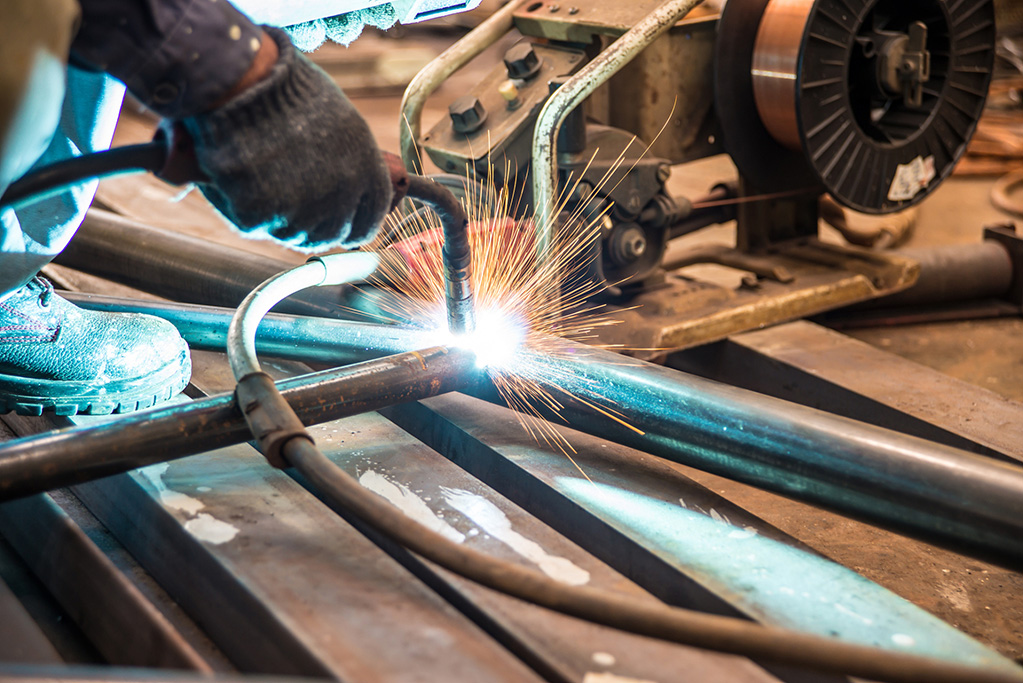

Welding
Argon is used as a protective gas in the welding process to avoid the burning of alloying elements, ensuring that the metallurgical reaction in the welding process is simple and easy to control, thus ensuring the high quality of the welding. Argon shows superiority in welding stainless steel, magnesium, aluminum and other alloys, and is often used in argon arc welding.
Metallurgy And Metal Processing
It is widely used in aluminum, magnesium, as well as titanium, zirconium, germanium and other special metals smelting, especially when blowing special steel, which can improve the quality of steel. During metal smelting, argon is used to create an inert atmosphere that prevents the metal from being oxidized or nitrided. For example, in the manufacture of aluminum, argon is used to create an inert atmosphere that helps remove soluble gases from molten aluminum.

Semiconductor Manufacturing ProcessING
High purity argon is used in semiconductor manufacturing processing chemical vapor deposition, crystal growth, thermal oxidation, epitaxy, diffusion, polysilicon, tungstic, ion implantation, current carrier, sintering, etc. Argon as a protective gas for the production of single crystal and polysilicon, can improve the quality of silicon crystals. High purity argon can be used as an inert gas for system cleaning, shielding and pressurization, and high purity argon can also be used as chromatographic carrier gas.
New Energy Industry
Provide gas raw materials needed for the preparation of new energy materials, battery production and other links, and create an inert gas environment.

Illumination INDUSTRY
In the manufacture of fluorescent tubes and liquid crystal displays, argon is used as a filling or process gas to facilitate the production of efficient and stable luminous effects and high-quality display panels.
Medical Use
Argon has a variety of applications in medicine, such as high-frequency argon knives and argon-helium knives, which are used to treat tumors. These devices make qualitative changes in the internal structure of the tumor through the methods of freezing and heat exchange, so as to achieve the therapeutic effect.
 Phone:
0086-15531448603
Phone:
0086-15531448603 E-mail:elena@hznuzhuo.com
E-mail:elena@hznuzhuo.com






